21+ bromine bohr diagram NikitaKrystyna
Bromine is the 3 rd lightest halogen in the periodic table. Bromine is in liquid state and it is 3 times denser than water. Bromine is the 44 th most abundant element present in the earth's crust. Bromine is present in the earth's crust at a concentration of 2.4 ppm. Pure bromine is toxic and it can burn the skin.
bromine electron configuration DrBeckmann
The Naked Scientists Periodic Table of Videos Created by video journalist Brady Haran working with chemists at The University of Nottingham. Element Bromine (Br), Group 17, Atomic Number 35, p-block, Mass 79.904. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.

Bohr Model Bromine
To write the orbital diagram for the Bromine atom (Br) first we need to write the electron configuration for just Br. To do that we need to find the number o.

Bohr Model Representation Bromine Atom Number Stock Vector (Royalty
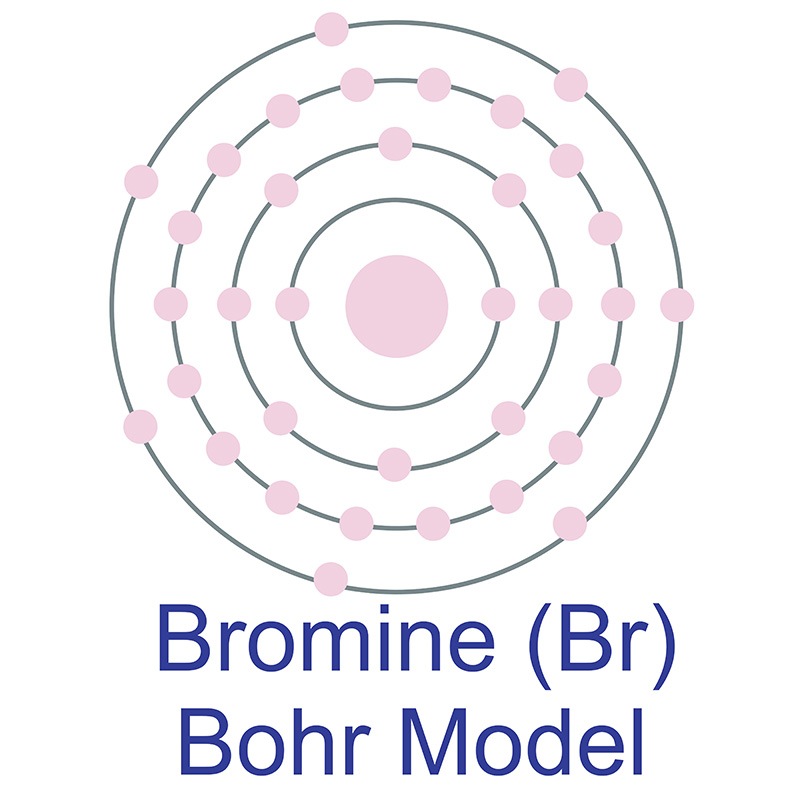
Right? You have already seen the bohr model of bromine atom in the above table. From the Bohr model, it can be found that the number of orbits or shells in bromine is 4. Hence, as bromine has 4 orbits, it lies in period 4 of the Periodic table. Why is Bromine in p-block? Before knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question.
Bromine Bohr Diagram
#1 Using aufbau principle #2 Using periodic table #3 From its Bohr model #4 From its orbital diagram Let's break down each method in detail. Using aufbau principle First, find electrons of bromine atom Periodic table The atomic number of bromine represents the total number of electrons of bromine.
Bromine Bohr Diagram
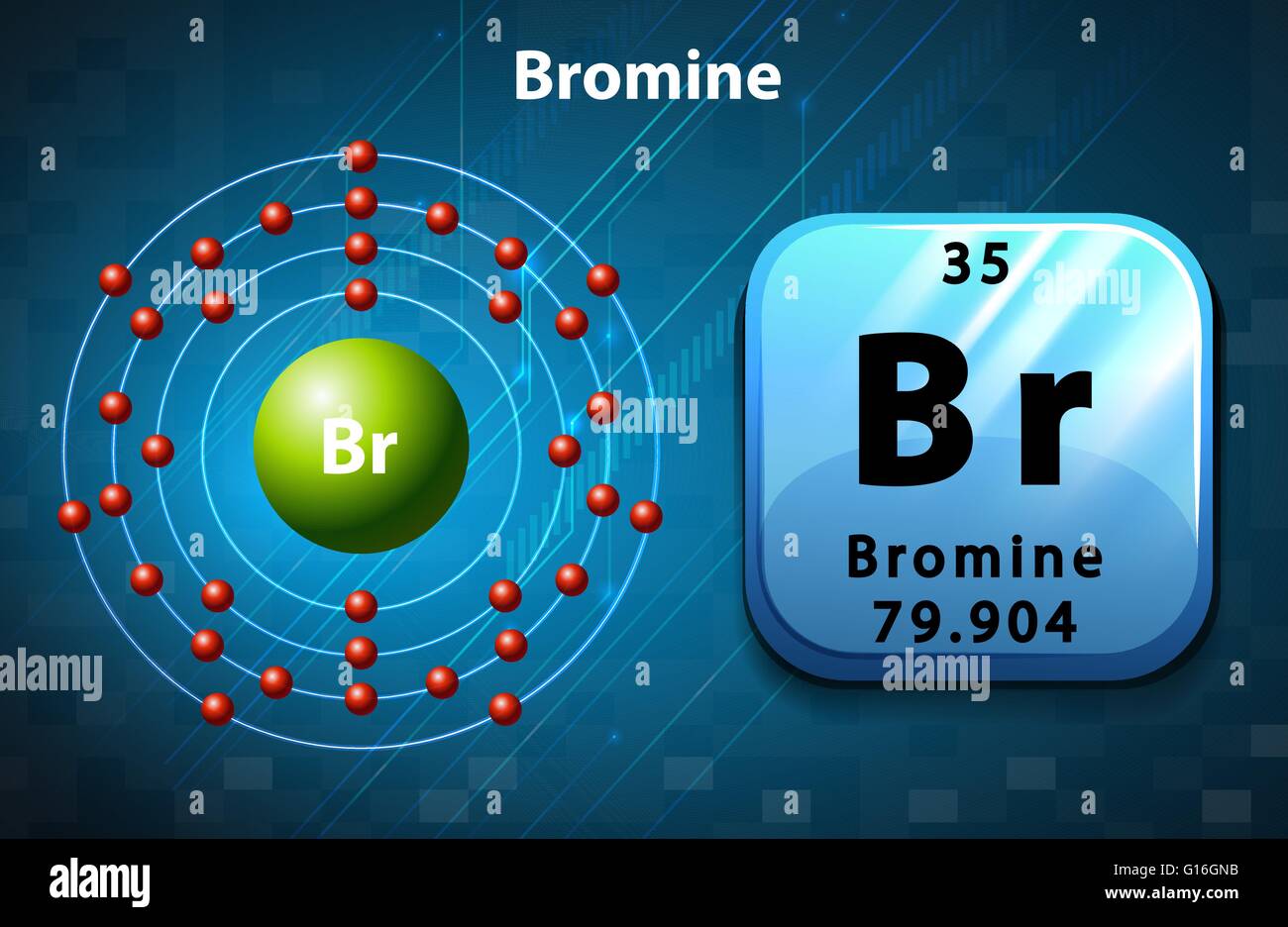
Basic Information Name: Bromine Symbol: Br Atomic Number: 35 Atomic Mass: 79.904 amu Melting Point: -7.2 °C (265.95 K, 19.04 °F) Boiling Point: 58.78 °C (331.93 K, 137.804 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 35 Number of Neutrons: 45 Classification: Halogen Crystal Structure: Orthorhombic Density @ 293 K: 3.119 g/cm 3 Color: Red Atomic Structure

Chemist Atom of Bromine Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of
On the far left of Figure 3.6.1 3.6. 1 are the highest energy electromagnetic waves. These are called gamma rays and can be quite dangerous, in large numbers, to living systems. The next lower energy form of electromagnetic waves are called x-rays. Most of you are familiar with the penetration abilities of these waves.

7+ bromine bohr diagram RajibRajisha
The Bohr model of bromine contains a nucleus having 35 protons and 45 neutrons in the center, and around this nucleus, there are four electron shells containing 35 electrons. Contents Steps #1 Write protons, neutrons, and electrons of bromine atom #2 Draw nucleus of bromine atom #3 Draw 1st electron shell #4 Draw 2nd electron shell
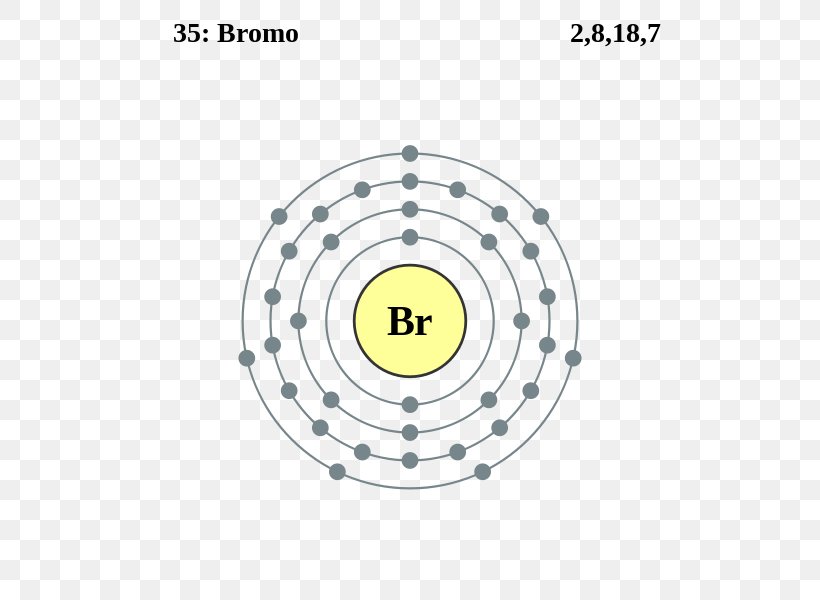
Electron Configuration Bromine Chemical Element Electron Shell Bohr
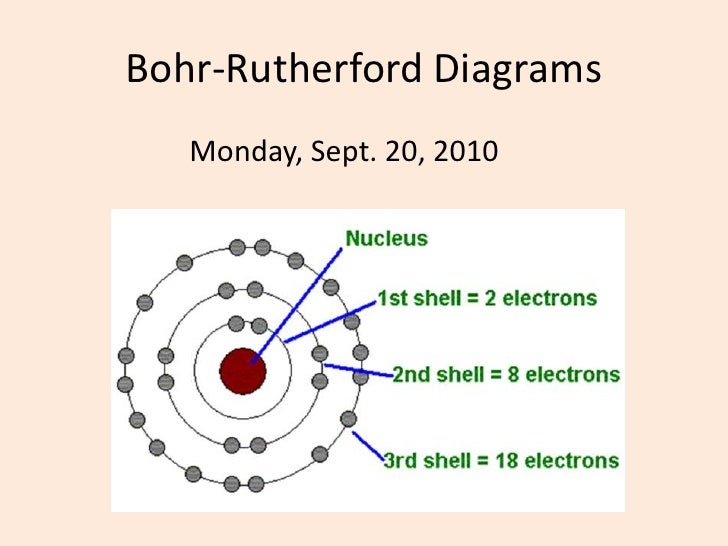
Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons are pictured as traveling in circles at different shells, depending on which element you have. Figure 2 2 contrast the Bohr diagrams for lithium, fluorine and aluminum atoms. The shell closest to the nucleus is.
Bromine (Br) AMERICAN ELEMENTS
Bromine. Launch. Subject: General Chemistry. Animated. Breakable. VR Ready Web Ready. Bohr's Model of an Atom. The Bohr model describes the structure of an atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting in specific energy levels around it. Electrons can jump between these energy levels by absorbing or.

Bromine Facts Atomic Number 35 and Element Symbol Br
In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford-Bohr model of the atom, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, consists of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons.

Bromine Facts, Symbol, Discovery, Properties, Uses
A Lewis electron dot diagram (or electron dot diagram, or a Lewis diagram, or a Lewis structure) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the.
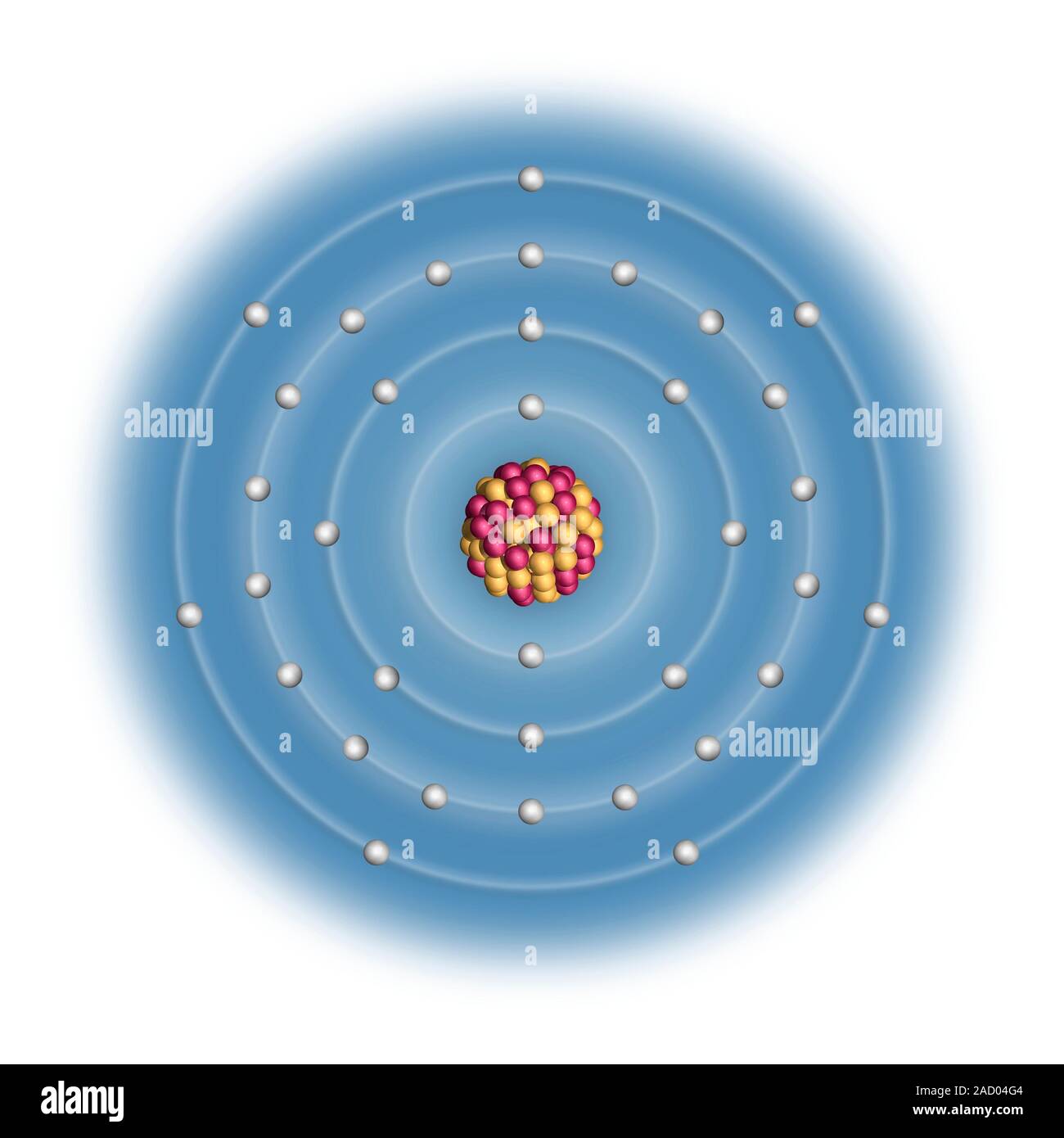
Bromine (Br). Diagram of the nuclear composition and electron
Electron configuration through orbit (Bohr principle) Electron configuration through orbital (Aufbau principle) Bromine (Br) electron configuration (Bohr model) Electron configuration through orbitals follows different principles. For example Aufbau principle, Hund's principle, and Pauli's exclusion principle.
Bromine Bohr Diagram
Here, we will draw the Bohr diagram of the Bromine atom with some simple steps. Steps to draw the Bohr Model of Bromine atom 1. Find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in the Bromine Protons are the positively charged particles and neutrons are the uncharged particles, both these are constituents of the atom nuclei.

How Can We Find A Electron Configuration For Bromine (Br)
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Lewis Structures. Solution; Lewis used simple diagrams (now called Lewis diagrams) to keep track of how many electrons were present in the outermost, or valence, shell of a given atom.The kernel of the atom, i.e., the nucleus together with the inner electrons, is represented by the chemical symbol, and only the valence electrons are drawn as dots surrounding the.

WebElements Periodic Table » Bromine » properties of free atoms
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table. 2). You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro. 3). You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE).